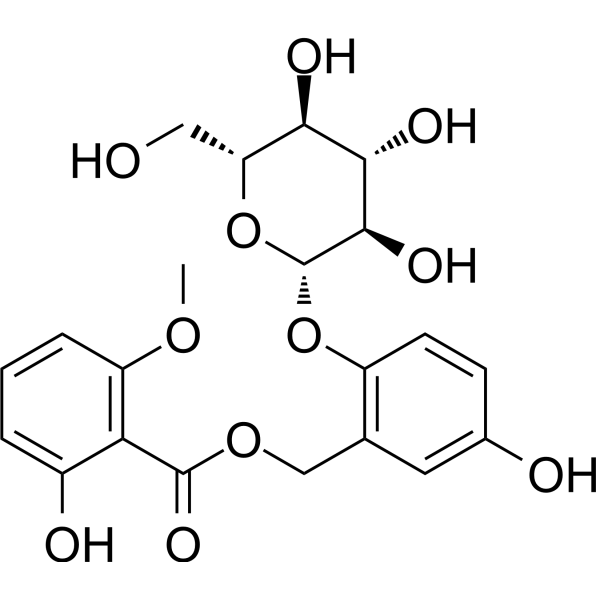
Curculigoside B
CAS No. 143601-09-6
Curculigoside B( —— )
Catalog No. M31660 CAS No. 143601-09-6
Curculigoside B shows antioxidative and antiosteoporotic activities, it can decrease area of bone resorption pit, osteoclastic formation and TRAP activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 135 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCurculigoside B
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCurculigoside B shows antioxidative and antiosteoporotic activities, it can decrease area of bone resorption pit, osteoclastic formation and TRAP activity.
-
DescriptionCurculigoside B shows antioxidative and antiosteoporotic activities, it can decrease area of bone resorption pit, osteoclastic formation and TRAP activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number143601-09-6
-
Formula Weight452.41
-
Molecular FormulaC21H24O11
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
2,3-Pentanedione
2,3-Pentanedione is a food additive that also occurs naturally as a fermentation product in beer, wine and yogurt and is released during the roasting of coffee beans.
-
NPAS3-IN-1
NPAS3-IN-1 is a potent inhibitor of NPAS3-ARNT heterodimerization, modulating NPAS3 transcription by targeting the interaction between NPAS3 and ARNT at the cellular level.
-
Xantphos
Xantphos, a ligand in the coupling reaction of Buchwald, Suzuki and others, is a metal chelating ligand that can be used to catalyze the reaction.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


